Problem:
输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构
Intuition:
树和链表都是典型的递归结构,遇到题目优先尝试从递归的角度来考虑。这个题目我们要找树A与B是否存在子结构的关系,那么这个过程可以分为两步。第一步,在树A中找到和树B的根节点一样的节点R;第二步,判断树A中以R为根节点的子树是不是包含和树B一样的结构。
Solution:
1 | public class CodingInterview_026 { |
输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构
树和链表都是典型的递归结构,遇到题目优先尝试从递归的角度来考虑。这个题目我们要找树A与B是否存在子结构的关系,那么这个过程可以分为两步。第一步,在树A中找到和树B的根节点一样的节点R;第二步,判断树A中以R为根节点的子树是不是包含和树B一样的结构。
1 | public class CodingInterview_026 { |
输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
1 | public class CodingInterview_025 { |
输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
我们要用递归的思路完成这个问题,那么第一个节点原来应该指向的是第二个节点,现在指向的是null.对于第n个节点来说,原来指向的应该是第n+1个节点,现在应该指向的是第n-1个节点.那么这个递归关系如何进行构建?实际上问题就变成了我知道如何变换一个长度为n-1的反向链表(利用递归的特性),如何在它前面加一个节点然后拼起来的问题。想象一下从n-1个节点到n个节点的拼装的过程,问题就明确了。
1 | public class CodingInterview_024 { |
给一个链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,输出null。
设置快慢指针,都从链表头出发,快指针每次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,假如有环,一定相遇于环中某点(结论1)。接着让两个指针分别从相遇点和链表头出发,两者都改为每次走一步,最终相遇于环入口(结论2)。以下是两个结论证明:
两个结论:
1、设置快慢指针,假如有环,他们最后一定相遇。
2、两个指针分别从链表头和相遇点继续出发,每次走一步,最后一定相遇与环入口。
证明结论1:设置快慢指针fast和low,fast每次走两步,low每次走一步。假如有环,两者一定会相遇(因为low一旦进环,可看作fast在后面追赶low的过程,每次两者都接近一步,最后一定能追上)。
证明结论2:
设:
链表头到环入口长度为–a
环入口到相遇点长度为–b
相遇点到环入口长度为–c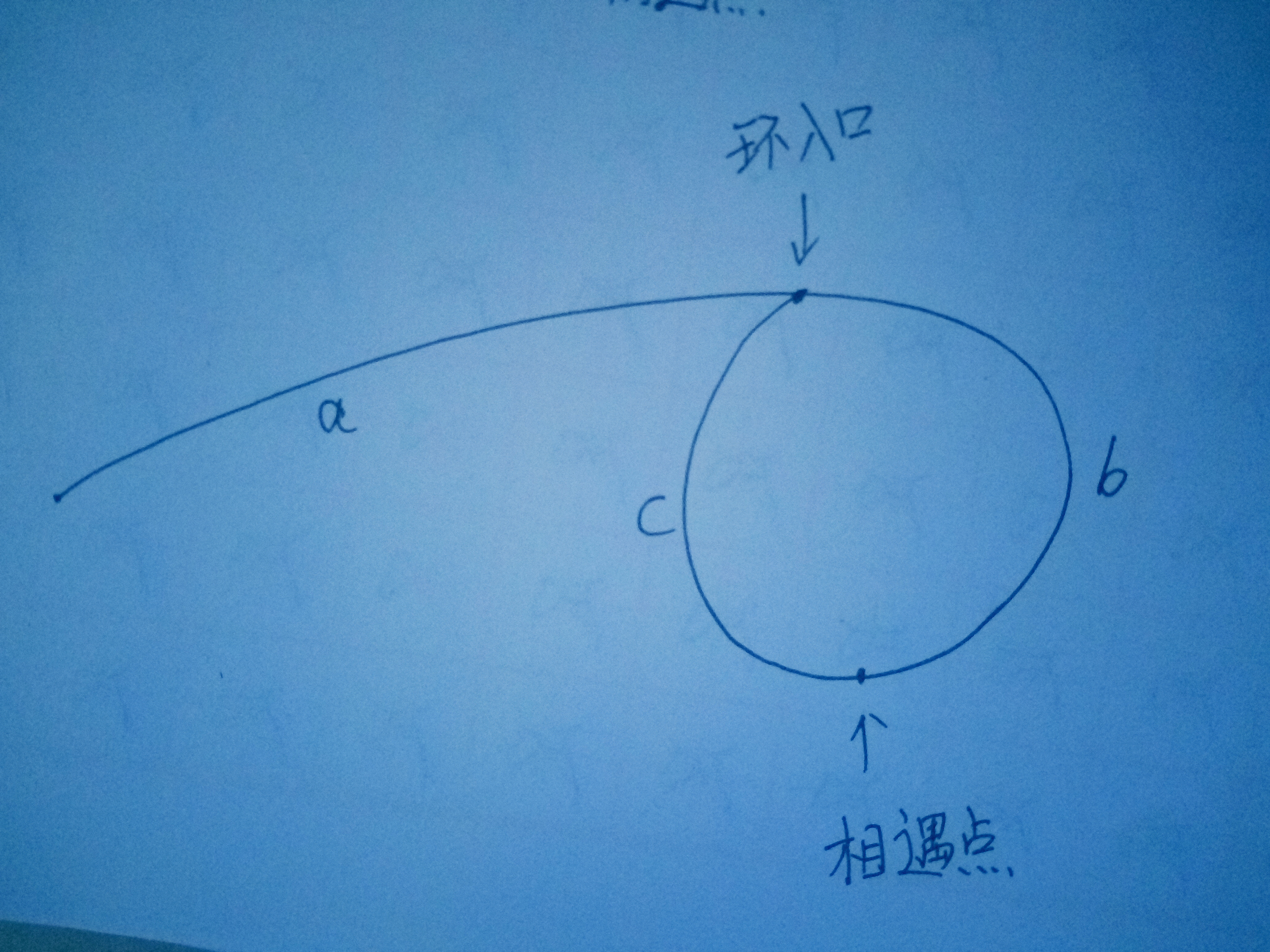
则:相遇时
快指针路程=a+(b+c)k+b ,k>=1 其中b+c为环的长度,k为绕环的圈数(k>=1,即最少一圈,不能是0圈,不然和慢指针走的一样长,矛盾)。
慢指针路程=a+(b+c)l+b ,k-l>=1
快指针走的路程是慢指针的两倍,所以:
a+(b+c)k=2[a+(b+c)l+b]
化简可得:
a=(k-l)(b+c)+c 这个式子的意思是: 链表头到环入口的距离=相遇点到环入口的距离+(k-l)圈环长度。其中k>=1,所以k-l>=0圈。所以两个指针分别从链表头和相遇点出发,最后一定相遇于环入口。
1 | public class CodingInterview_023 { |
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
设链表的长度为 N。设置两个指针 P1 和 P2,先让 P1 移动 K 个节点,则还有 N - K 个节点可以移动。此时让 P1 和 P2 同时移动,可以知道当 P1 移动到链表结尾时,P2 移动到第 N - K 个节点处,该位置就是倒数第 K 个节点。
1 | public class CodingInterview_022 { |
输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
这个题目比较容易,我们只需要知道整个数组中奇数有多少个,然后分开分别进行存放就可以了。
1 | public class CodingInterview_021 { |
请实现一个函数用来判断字符串是否表示数值(包括整数和小数)。例如,字符串”+100”,”5e2”,”-123”,”3.1416”和”-1E-16”都表示数值。 但是”12e”,”1a3.14”,”1.2.3”,”+-5”和”12e+4.3”都不是。
首先我们来看一下题干里面的数字有哪些特点,不难发现所有的数字都可以大体写成整数+符号(小数点或者E,e)+整数的形式(如果第一个符号是小数点还可能出现第二个符号是e,但是总体来说不会出现比这种情况更复杂的情况了)。实现的时候我们要注意两个点。1.最好用一个全局变量index来存当前扫描到的下标,否则不断对下标进行传参或者进行数组的拷贝很麻烦也很容易出错。2.在进行其他判断之前都要判断数组是否越界,养成良好的习惯。
1 | public class CodingInterview_020 { |
删除链表中重复的结点
1 | public class CodingInterview_019 { |
在 O(1) 时间内删除链表节点
① 如果该节点不是尾节点,那么可以直接将下一个节点的值赋给该节点,然后令该节点指向下下个节点,再删除下一个节点,时间复杂度为 O(1)。
② 否则,就需要先遍历链表,找到节点的前一个节点,然后让前一个节点指向 null,时间复杂度为 O(N)。
综上,如果进行 N 次操作,那么大约需要操作节点的次数为 N-1+N=2N-1,其中 N-1 表示 N-1 个不是尾节点的每个节点以 O(1) 的时间复杂度操作节点的总次数,N 表示 1 个尾节点以 O(N) 的时间复杂度操作节点的总次数。(2N-1)/N ~ 2,因此该算法的平均时间复杂度为 O(1)。
1 | public class CodingInterview_018 { |
输入数字 n,按顺序打印出从 1 到最大的 n 位十进制数。比如输入 3,则打印出 1、2、3 一直到最大的 3 位数即 999。
由于 n 可能会非常大,因此不能直接用 int 表示数字,而是用 StringBuffer进行存储。既然是用StringBuffer来存,那么我们就要完成两个功能,第一个功能是如何对使用char数组存储的数字进行递增,第二个功能是如何将该数字打印出来(这个部分的核心代码主要是去掉符号扩展自动补上的0).
1 | public class CodingInterview_017 { |